- Introduction
- Limitations
- New naming convention
- Installation / Configuration
- Addon installation
- Prepare and upgrade
- Upgrade (or downgrade) from one version to another
- How does the Remote Upgrader work ?
- Upgrade / Downgrade tests
- Conclusion
Introduction
Here is a quick review of the Remote Upgrader Feature provided with the brand new Splunk version 10, that was released in July.
This new feature allows you to upgrade (or downgrade) your Agents distributed across your Splunk infrastructure managed by your Agent Management, formerly known as Deployment Server.
Limitations
There are not a lot of limitations, but still:
- it is limited to Splunk Universal Forwarder, version 8 to 10
- supported only on Linux platforms
- needs a specific addon and a specific configuration
New Naming Convention
A good to know information, if you didn’t notice it: the Deployment Server and Clients are now renamed as Agent Management and Agents.
You can find this information here: https://help.splunk.com/en/splunk-enterprise/administer/update-your-deployment/10.0/agent-management/about-agent-management
Installation / Configuration
Addon installation
First of all, as this feature is depending on an addon, you have to download it from Splunkbase:
- Download and untar the Remote Upgrader for Linux Universal Forwarders on splunkbase.com.
- On the Agent Management, copy the package from the default folder
/opt/splunk/etc/deployment-apps/splunk_app_uf_remote_upgrade_linux/default/packages/splunk-upgrader-{version}.tgzand/opt/splunk/etc/deployment-apps/splunk_app_uf_remote_upgrade_linux/default/packages/splunk-upgrader-{version}.tgz.sig
to the local folder/opt/splunk/etc/deployment-apps/splunk_app_uf_remote_upgrade_linux/local/packages/ - Deploy the app by affecting it to a Server Class.
NOTE: the remote upgrader for Linux Universal Forwarder is not a Splunk add-on. It's a mechanism you use to deliver the Agent package and/or the Remote Upgrader package to remote Agent boxes. It runs as a separate Linux service outside of the Splunk home directory.
It always requires ROOT to install, so Agent and Agent Management cannot install the remote upgrader.
You can install the Remote Upgrader for Linux as an existing user or by creating a new one.
You have to untar the the app you previously copied to the local/packages directory (in step 2):
tar zxvf /opt/splunkforwarder/etc/apps/splunk_app_uf_remote_upgrade_linux/local/packages/splunk-upgrader-linux-102.tgz -C /var/tmp
You can untar in the directory you want, here /var/tmp, then go to that directory and run the following command:
/var/tmp# sudo ./bin/install.sh --accept-license --create-user/var/tmp# sudo systemctl start splunk-upgrader
You can verify the status:
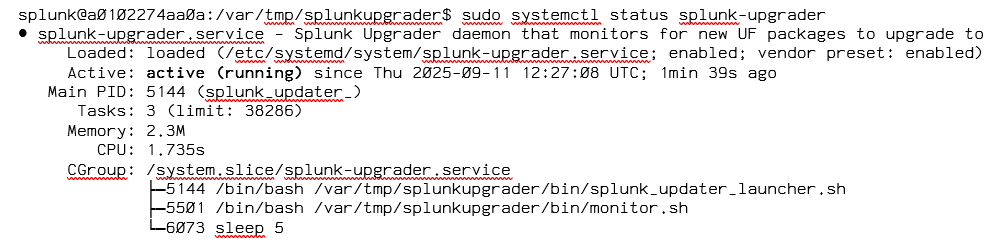
The setup is then finsihed.
NOTE for Docker users: this addon cannot be tested in Splunk dockers as it requires systemctl. If you want to test with Docker, I advise you to use a Ubuntu docker for the forwarder, and configure it to use systemctl, then install a Splunk Agent on it and connect it to the Agent Management.
Prepare and upgrade
You can set up delivery using an Agent Management or a third party delivery product as follows:
Download the universal forwarder package and signature and insert them into the delivery app at ./local/packages/ dir, then deploy it with the Deployment Server Agent Management.
- Update your
local_configand deploy it using the Agent Management. See Modify remote upgrader using the configuration files for more information.
- Use the Agent Management to deliver the Splunk Remote Upgrader for Linux package.
Upgrade (or downgrade) from one version to another
You have to download from Splunk Website the Universal Forwarder package. you also need to download the x509 signature for the package you choose.
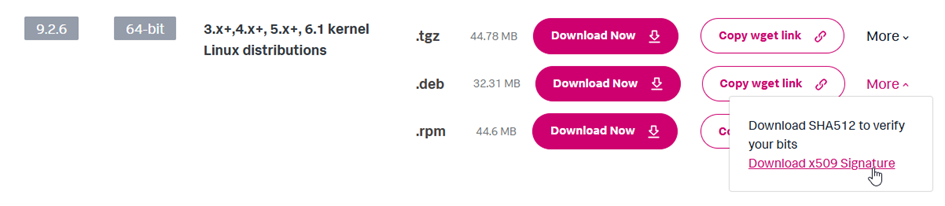
Downlad the X509 certificate that you will rename as the name of the packet +.sig at the end. If you download the splunkforwarder-9.2.6-bfd122d7f8fc-linux-2.6-amd64.deb package, then create the splunkforwarder-9.2.6-bfd122d7f8fc-linux-2.6-amd64.deb.sig file and put the X509 certificate inside. You can get the Certificate on the same page as your Splunk Agent download, by clicking on the “More” button.
How does the Remote Upgrader work ?
Place these 2 files under local/packages of the splunk_app_upgrader_delivery (under /opt/splunk/etc/deployment-apps).
Then to start the upgrade, just trigger a new delivery of the app to the Agent.
/opt/splunk/bin/splunk reload deploy-server
Then, behind the scenes, Splunk copies the new Agent package to the /tmp/SPLUNK_UPDATER_MONITORED_DIR directory and creates a file named “start_uf_upgrade” which triggers the update of the Agent.
Upgrade/downgrade tests
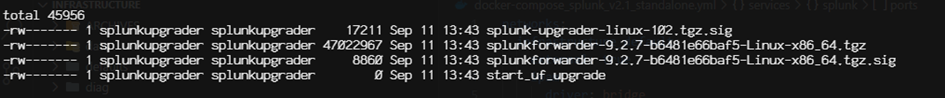
Example of the /tmp/SPLUNK_UPDATER_MONITORED_DIR directory during an upgrade/downgrade (here version 9.2.4):
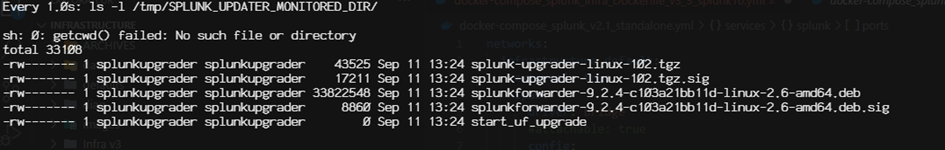
If you have 2 different versions of the Agent package, apparently only the last one is considered (to be verified).
The Agent is then updated and some minutes after you have your Agent version upgraded in the Agent Management (Deployment Server):

You can also downgrade your Agent by putting a previous version in the local/packages directory. On the previous screenshot, the version 9.2.6 was just upgraded from 9.2.4.
For testing purposes, I replaced the 9.2.6 with the 9.2.4 in the local/packages and triggered a new deployment with splunk reload deploy-server on the Agent Management.
Downgrade :
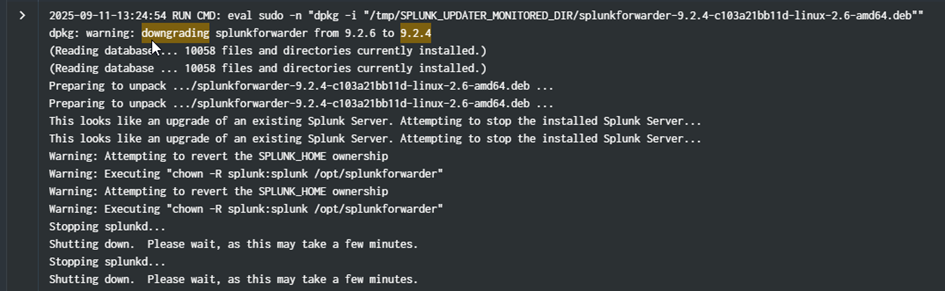
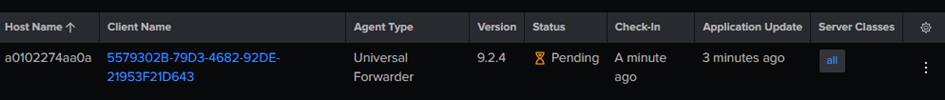
The version was replaced, but pending. It took time but finally got it back to OK.

New upgrade
I decided to upgrade again, to version 9.2.7.
I put the right packages in local/packages then triggered a new upgrade (with the tgz file this time, instead of .deb package). But I got the following error message in the logs:
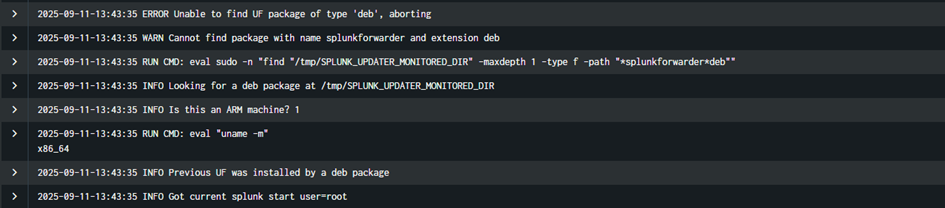
So it is mandatory to keep the same type of package you used to upgrade the Agent at the beginning. All logs about the upgrade is available with that query:

Conclusion
This Remote Upgrader is working well. It requires ROOT permissions to be installed and a specific or existing user to operate. But it is working well. You can find additional information on the Remote Upgrader for Linux Universal Forwarders page. Preparing the Agent packages is a manual thing to do, and still needs a way to push the Remote Upgrader addon to the Agent, and requires an access on the Agent to install it.
The time for the agent to get back to an OK status can be strange at some point. I only tested with one Agent, so upgrading several or a high number of Linux Agent can be different from the experience described in this article. Please test in DEV/PREPROD environments before going to production (as always).

Thank you for this article. It helps a lot.